
The digital world is ever evolving and has brought forth a multitude of new tech aimed at making human lives easier. Face technology is the new invention that is designed for detection of human faces. Replacing the commonly preferred fingerprint sensor, Face technology is among the fastest biometric technology. It is able to scan and detect one’s face by recording the distance between several facial features. Here, the human face acts as the identifier. Place your face in front of the camera and allow it to scan.
Face technology easily replaces the palm scanner where you are required to place your palms on a scanner glass and wait for the scan to complete. This is not a common practice as people shun from this practice citing it as a source of illness spreading. Other methods include the IRIS scanner which require you to position your eyes precisely in front of the scanner.
Face Technology, on the other hand, is capable of scanning your face without invading your personal space. This is achieved by putting together the collective data from a collection of cameras that capture your face. This technology measures all the features of your face which includes
With the advancement of Deep Neural Networks (DNN) coupled with face scanning cameras, this technology has made its way into the conventional sector. A good understanding of Face technology is necessary when it comes to employing this technology.
On a broader spectrum, face technology is classified into face detection and face recognition. Although their underlying principle might be the same, face recognition takes this technology a notch higher.
Face detection is the process where a computer is able to identify the presence of a human face within a digital picture. This is made possible with the help of machine learning and complex algorithm which will be explained in detail in the subsequent sections.
“Eyes are windows to one’s soul” applies to face detection as eyes are the first thing this tech looks for in a face. Eyes comprise of the valley region, one of the easiest to detect. Following the eyes, the algorithm scans for facial features like the nose, mouth, and jaw. After the algorithm zeroes in on a face, other tests can be applied to determine the authenticity of its detection.
The advanced application of face detection is face recognition. The difference between them is, face recognition utilizes the detected data and attempts to identify the owner of the face.
This is a complex process that uses computers and cameras to identify a person’s face and runs it on a database containing face data. The resultant matching file is then displayed. The accuracy of the result is questionable, however, it will help in narrowing down the search to those that have high chances of matching with the target.
Some of the applications include
A typical face detection and recognition process are described in the flowchart.
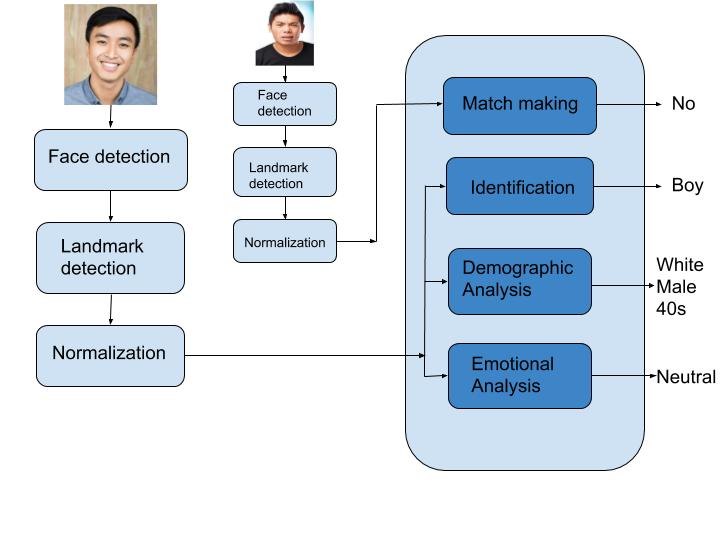 The input data is usually fed from the image captured on a camera. Brownie points if the camera used contains depth effect as it can make the detection much easier. The camera is ensured to be placed at the perfect angle to capture all aspects of the face leaving no room for errors.
The input data is usually fed from the image captured on a camera. Brownie points if the camera used contains depth effect as it can make the detection much easier. The camera is ensured to be placed at the perfect angle to capture all aspects of the face leaving no room for errors.
Detection starts by scanning the human face that is present in front of it. All the detected faces are marked with a “Face detector box”. After identification, the coordinates of the face is marked and the box is removed.
Face detectors are quite adept at picking out faces even from an image that is hosting a large group of people. The challenge is in identifying faces that are further away, typically smaller faces and the ones that are not properly photographed. In such cases, the technological barrier is overcome by implementing deep learning.
Post determining the location of the face, facial landmarks are marked. This refers to features such as jawline, eyes, eyebrows, mouth, and nose. DLIB is a commonly used source image processing toolkit. It works by tracking 68 key points on a face. This allows it to keep track of the face even if it is tilted or rotated.
Landmarks satisfy the purpose of normalizing the image. Normalization enhances the recognition process by extracting only the face from the image. This data forms the core of face swap feature offered in Snapchat and Facebook.
The face that is detected differs in its size, brightness, and features. This can bring about a significant change in successfully detecting the face. To eliminate the chances of failure, normalization is performed. Eyes are the basic feature points selected from the center points and that is where the process begins.
In addition to face normalization, brightness is normalized by grey information. Information that is useless, irrelevant, and redundant such as objects in the background, hair, glasses, makeup are ignored in this process.
The normalized images differ from each other by a small degree and the computer is taught to distinguish between them. An advanced form of deep neural network (DNN) called the convolutional neural network (CNN) is employed for this purpose.
The CNN is initially fed with normalized data of hundreds of faces. With this, the system learns to tell the difference between different faces by identifying and comparing over 100 features of the images. By comparing the images from same people with different people, CNN can tell the faces apart.
The data obtained is stored in a secure storage dubbed neural network model which coincidentally is also used in identification and detection. When your face is listed in the network, it can be freely accessed by the model.
The more the merrier is true in the case of face detection. The size of a neural network is a prime factor when it comes to detecting faces. This is also the reason why Baidu and Facebook’s face recognition is such a hit albeit being severely frowned upon. This algorithm is said to be as accurate as humans in identifying the people tagged on posts.
Besides analyzing one’s face, the system can also be tuned to garner additional information from the image such as age, sex, emotion, and any additional accessory equipped on the face.
Perhaps the best compendium of facial data is the Labelled Face in the Wild (LFW) The project is aimed at producing Receiver Operating Characteristic (ROC), a common parameter that is used as a performance metric for classification tasks. The optimum parameter can be determined to form ROC and is considered for segmentation analysis. ROC is used to give true or false results and is used for binary classifiers.
Similar tests were performed on humans and the results obtained were inferior.
Face recognition technology has been in research since 1964 and in 1966 a scalable version of the same was built. Up until 1997, face recognition technology was unavailable to the public. The ZN-Face developed was used by customers in the Deutsche Bank and airport operators. In 2006 the face recognition algorithms were evaluated by Face Recognition Grand Challenge (FRGC) and are touted to be 100 times better than ZN-Face. With the recent advancements in camera technology, it is only fair that we take the next step in technology - Implementing face recognition technology for day to day usage.
As the gap in skill between a computer and human face identification grew shorter, it only made sense to implementing face detection for commercial usage. The MegaFace data sheet contains over a million registered faces and has been widely used as a test sample for algorithms. Various organizations performed tests and the most fruitful of them was Google’s FaceNet which provided an accurate detection of up to 75% for a small group of people.
Equipped with an ever-expanding base, the accuracy of the system only gets better with additional data.
Platforms such as SaaS which is cloud-based can be utilized to develop and deliver this software on a much larger scale. Application programming interface (API) and software development kit (SKD) offer facial integration solutions. Competitive pricing has let to developers pricing their solutions moderately on the price spectrum.
The number of companies offering facial recognition is on the rise meaning a reduction in purchase and running cost is imminent. This makes it possible for facial recognition technology to be implemented as a replacement for everyday things such as door locks and home safes.
With the facial recognition improving at breakneck speed, it is only fair that the technology advances in all aspects. Improving the speed of detecting is one such crucial thing. Being able to quickly detect and identify faces will make the call in choosing between various applications of the system.
Airports can employ face detection to eliminate long waiting time and crowd management with a quicker identification of undesirable individuals on a crowded street will make a world of difference.
There is a multitude of facial recognition technology solutions that developers can choose from. Each comes with their own pros and cons. They can be largely classified into Cloud-based and Offline SDK.
Touted as beginner friendly, cloud-based solutions are where you turn to for experimentation. The greatest advantage is that this system can perform with bare minimum specification thanks to free evaluation and development
| Features | Platforms | |
| Face++ | Face Landmark
Face Compare |
iOS
Android |
| Kairos | Face Analysis (Includes age, gender, facial landmark, detection, emotion, sentiment analysis)
Face Recognition (Includes verification and identification) |
Windows
Linux OSX Android iOS Pi ChromeOS |
| Affectiva | Emotion Analysis (Includes age, gender, ethnicity classifiers) | Windows
Linux OSX Android iOS Pi ChromeOS |
| Luxand | Face Recognition
Face Detection Facial landmark detection |
Linux
Windows iOS Android OSX |
| SightHound Sentry | Face Detection (Includes age, gender, emotion analysis and facial landmarks)
Face Recognition (Includes grouping and authentication) |
iOS
Windows Linux OSX |
The greatest advantage of running an offline service is security. The images need to be sent to a third party for identification which raises a red flag for the customers. Although they claim to format the data, one can never be too careful as the image always tends to be backed up to their facial recognition system. Offline SDKs are the best alternative.
The success of an Offline SDK largely depends on the capability of the hardware. A list of SDK providers and the corresponding features respective to their platforms is charted out below.
| Features | Platforms | |
| Face++ | Face Landmark
Face Recognition |
iOS, Android |
| Kairos | Face Analysis (Includes age, gender, facial landmark, detection, emotion, sentiment analysis)
Face Recognition (Includes verification and identification) |
Windows, Linux, OSX, Android, iOS, |
| Affectiva | Emotion Analysis (Includes age, gender, ethnicity classifiers) | Windows, Linux, OSX, Android, iOS, |
| Deepsight | Face Recognition
Face Detection Facial landmark detection Face Demographics |
Linux
Windows |
| SightHound Sentry | Face Detection (Includes age, gender, emotion analysis and facial landmarks)
Face Recognition (Includes grouping and authentication) |
iOS, Windows, Linux, OSX |
Open source libraries such as OpenCV or CCV allow license-free usage for both educational and commercial uses. These libraries assist the developer to convert the data gathered into full-fledged applications.
When it comes to facial technology application, the Chinese are a class apart. Face++ a billion-dollar Chinese institution is a pioneer when it comes to face technology. With its help, there already has been a significant breakthrough in how people make payments and how people are identified.
Alipay, a popular payment portal allows people to authorize payments with their face. This has revolutionized the way money is transferred .
Ride-hailing company, Didi also facilitates the use of face technology to determine the authenticity of the person behind the wheels. This system connects itself to the intricate web of cameras. The most benefited, however, are the law enforcement department. Face recognition technology is actively used to identify and determine the location of suspicious people. It even goes as far as alerting the cops much like “The Machine” portrayed in the famous sitcom, Person of Interest.